Arrays in C language
An array in C language is defined as a finite and ordered collection of similar data types which get stored in contiguous memory locations.
finite: The range of data must be defined.ordered: The data must be stored in some order and C compiler store data as continuous memory addresses.
Important points to remember:
- Arrays are the derived data type in C which can store the primitive type of data such as int, char, double, float, etc.
- We can access any element randomly in an array by using its index number.
- The index number starts from zero (
0) and increment by one tillsize - 1. - Each element of an array is of same data type and carries the same size. For example, if data type is
intthen each element is of4 bytes.
Syntax
The following is the syntax for declaring an array.
type arrayName [ arraySize ];
where
arraySizemust be an integer and must be greater than zero.typeis a valid C data type.
This is called a single-dimensional array.
Example
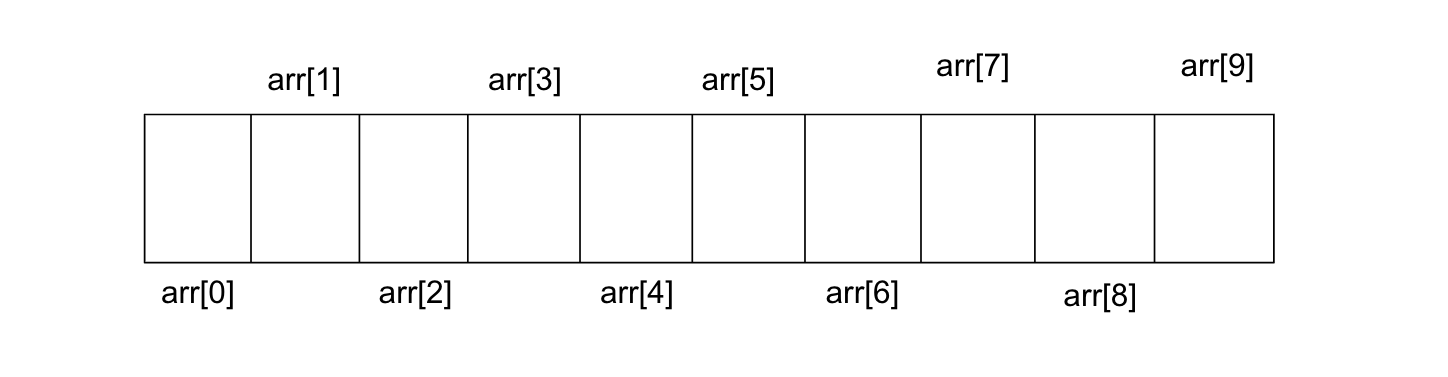
int arr[10]; // create an array with 10 integer elements
Declaration with initialization
We can also initialize an array during its declaration.
int evens[5] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}; // array of 5 even numbers
Access Array Elements
We can access any element of an array by its index number.
Syntax:
arrayName [ indexNumber ];
For example, to access elements from evens array as defined above, we can use following:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int i, evens[5] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("evens[%d] = %d\n", i, evens[i]);
}
return 0;
}
// output
evens[0] = 2
evens[1] = 4
evens[2] = 6
evens[3] = 8
evens[4] = 10
Help me to improve BRG Trainings.